What Are the Treatments Regarding Pneumonia Disease?
According to the American Lung Association, pneumonia is a lung infection and a common complication in people with COPD. It is also the leading cause of death among children under five years old.
The World Health Organization (WHO), on its website, says that pneumonia kills an estimated 600,000 people every year. That means that, in a year, more than one million people die from this disease worldwide. In the United States, it causes around 1.4 million deaths each year.
People who have a weakened immune system are at greater risk for developing pneumonia. This includes people who have HIV/AIDS, those who have had cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy, or those who have been exposed to certain types of viruses such as influenza.
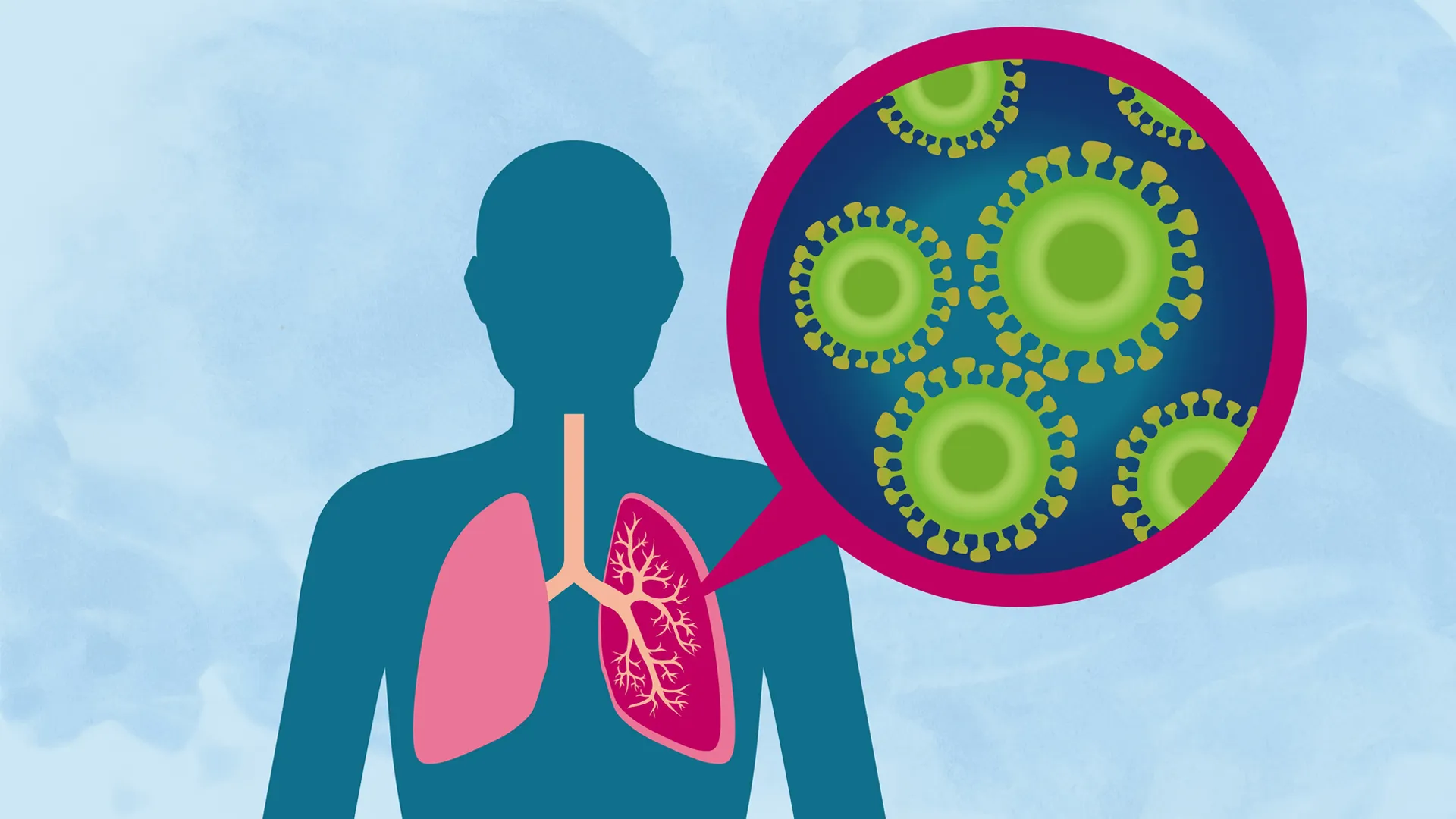
Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other germs that enter through the lungs. The symptoms usually begin with a cough that gets worse over time. Other signs may include fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid breathing, and trouble swallowing.
There are several ways that you can prevent getting sick with pneumonia. They include taking a daily multivitamin, eating foods rich in vitamin C (such as strawberries and green peppers), and making sure your body’s airways stay clear of mucus and debris with regular use of a neti pot.
If you do get sick with pneumonia, make sure you visit a doctor right away so they can prescribe antibiotics and start treatment as soon as possible. If you don’t receive prompt treatment for pneumonia, complications will occur and you could become very ill. These complications include respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death.
You may have a question which is pneumonia contagious then for that you have to check on the internet. But from our point of view it is in some of the people and in some are not. So you have to check it according to your body and feel of it then only you will be able to know more about your body.
How Pneumonia Is Diagnosed
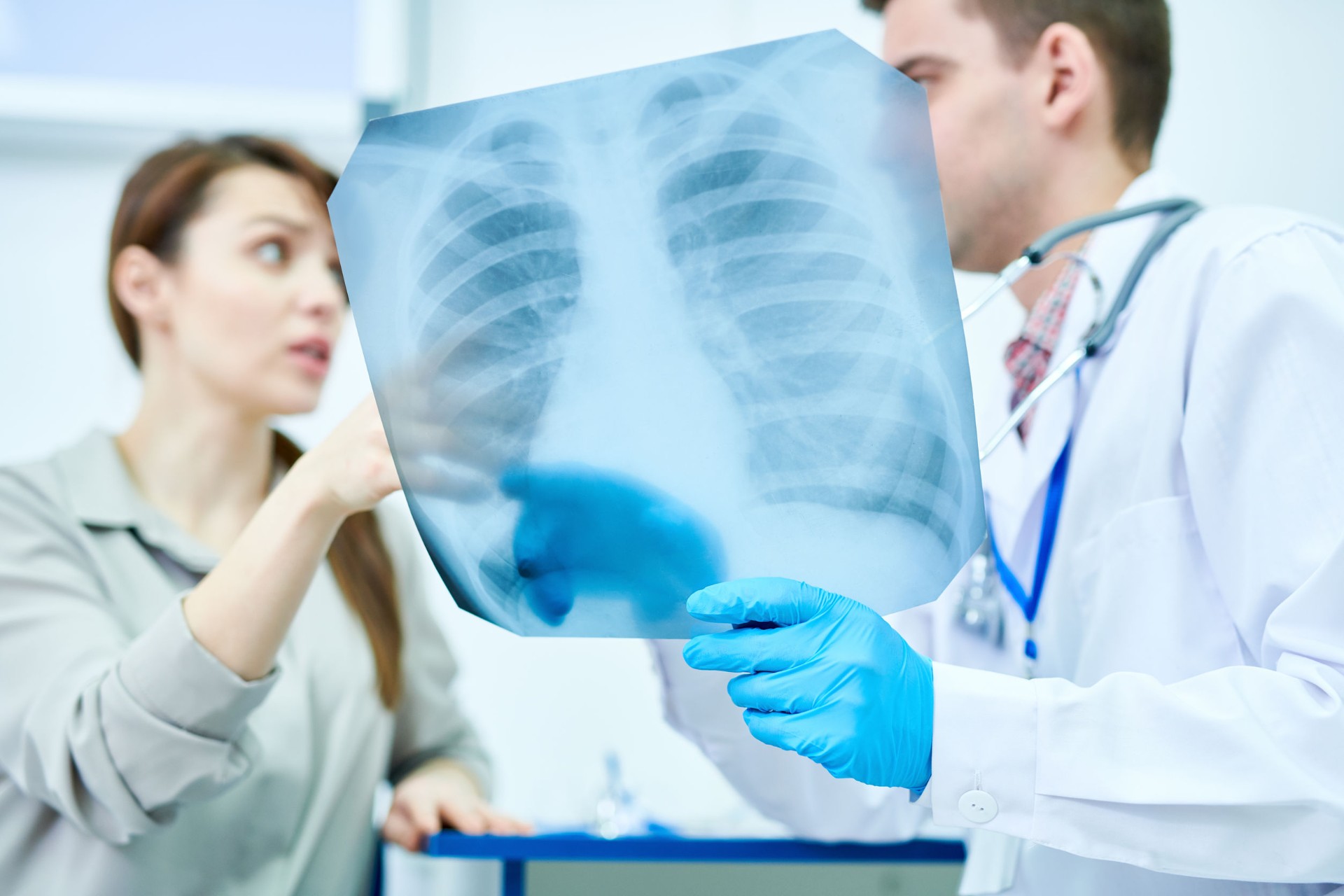
In order for doctors to diagnose pneumonia, they need to find out whether there is a bacterial, viral, fungal, or other type of germ responsible for the illness. A doctor will conduct tests to rule out other illnesses first before diagnosing pneumonia.
Doctors will check your medical history and look at your symptoms. They will then take a physical exam, which involves checking your heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, and weight.
A doctor will also ask about any recent travel to areas where there has been a high incidence of flu, especially if the symptoms began after traveling to these areas. Next, the doctor will take samples of fluid from the lower part of your throat called sputum to test for tuberculosis or any other infections.
Then, the doctor may conduct a CT scan or X-ray of your lungs to see if you have a bacterial infection. If not, your doctor may refer you to another specialist for further testing to determine whether you have pneumonia.
Treatment For Pneumonia
You should always consult a doctor when you notice new symptoms of illness such as a cough, fever, or difficulty breathing. Your doctor will be able to tell you more about how to treat your condition once he or she diagnoses it.
Your primary goal during treatment for pneumonia is to reduce your risk of bacterial infection. You should avoid smoking, since it increases your risk of developing severe cases of pneumonia because it reduces the amount of oxygen you can get into your bloodstream.
Once you start receiving treatment for pneumonia, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. When you take oral antibiotics, you swallow them whole. They typically last between three and seven days. There are some antibiotics that you can take intravenously, which means you inject them directly into your veins. This allows your body to absorb them faster and gives you better results.
When treating a patient with pneumonia, doctors often recommend prescribing two different kinds of antibiotics. One antibiotic should work against the germs causing the infection, while the second antibiotic works against the germs that already exist in the person’s body. The idea behind this approach is to prevent resistant strains of bacteria from emerging.
One important thing to remember when treating pneumonia is that antibiotics aren’t effective until the illness itself is treated. So, if you take antibiotics but still feel unwell, it could indicate that you still have an active case of pneumonia.
As mentioned earlier, you should not smoke. If you do smoke, your doctor may suggest using a nicotine patch or gum instead of quitting cold turkey. Doing so will help you wean off cigarettes slowly while minimizing withdrawal symptoms.
Another way to manage your health problems is by maintaining good nutrition. This includes avoiding fast food and processed food, choosing healthy snacks like fruits and vegetables, and drinking plenty of water. Eating well will keep you properly hydrated, which can help decrease your chance of having symptoms flare up again.
Lastly, you should make sure to practice good hygiene. This includes washing your hands frequently with soap, keeping your home clean, and practicing good personal habits like brushing your teeth twice per day.
Prognosis Of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. However, in most cases, the prognosis is fairly positive. As long as you follow the instructions listed above, you will recover completely.
However, if you ignore these tips and go back to smoking, you run the risk of getting sick again. Furthermore, if you develop a secondary infection along with the original illness, the prognosis becomes less favorable. As such, it is best to avoid going without proper care in the first place.
For more information about pneumonia and related topics, please read on!
Pneumonia is a major problem worldwide. According to the WHO, it killed 667,000 people in 2015 alone. That is almost half a million people more than the previous year. This number continues to rise due to increased rates of smoking in Western countries.
Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other germs that enter your body through your mouth, nose, or lungs. The symptoms usually begin with a cough that gets worse over time. Other signs of pneumonia include fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid breathing, and swallowing difficulties. There are various ways to prevent getting sick with pneumonia, including taking a daily multivitamin and eating foods rich in vitamin C (such as strawberries). If you do get sick with pneumonia, make sure you visit a doctor right away so they can prescribe antibiotics and start treatment as soon as possible.
There are many types of pneumonia. Viral pneumonia occurs when a virus enters your body and spreads throughout your body. This is why you might experience symptoms such as coughing, sore throat, sneezing, headache, fatigue, and diarrhea. Bacterial pneumonia occurs when the body’s defense mechanisms fail, allowing bacteria to enter your body and spread throughout your body. This kind of infection is sometimes referred to as “secondary” pneumonia because it occurs after a bacterial infection has already taken hold.
If you develop pneumonia, you should seek medical attention immediately. You should never try to cure the condition yourself. Instead, you should let your doctor know right away so they can prescribe antibiotics and start treatment as soon as possible. If you don’t receive prompt treatment for pneumonia, complications may arise. These complications include respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death.

